According to a recent report from the Kaizen Institute about efficient management of industrial assets, unplanned production stops represent a yearly cost of 50M€ to Industry. One of the most affected sectors is automotive, followed by mining / metalworking and producers of oil & gas. Following, we will go over the most common causes for these idle times and present applicable solutions for their mitigation.
Common causes for idle time
Lack of standardization in planning
In many companies, production planning exists in the mind of the production manager or in internally made Excel spreadsheets. However, as the company grows, this method of working becomes inefficient and, as a consequence, lack of transparency and loss of agility begins to appear, turning into a form of management typically known as "putting out fires".
Human error
We all make mistakes. In fact, the human being is one the most typical causes for idle time in manufacturing industry. This can be due to excess of workload, lack of experience and know-how, or insufficient procedures for carrying out the work.
Nevertheless, as with every failure-prone process, seeking to improve is essential, through the use of enablement programmes. Failure always brings an opportunity for improvement.
Lack of stock prevision
Without a forecast of available stock, replacement parts and other resources such as fuel, the manufacturing process can be stalled and result in idle time. Even a loss of power or other public services can interrupt the workflow and cause further idle times.
Maintenance inefficiencies
A high percentage of maintenance tasks are of a reactive nature, that is, they are geared towards repairing breakdowns, which is often due to an insufficient preventive maintenance.
In their most basic form, inefficient maintenance management comes from improper keeping of records and digitization - work done is not properly recorded, nor the materials and replacements used for maintenance. Lack of maintenance planning comes a close second. Without an adequate planning, there is no room for preventive maintenance.
Lack of follow-up learning and continuous improvement
To this day, many companies still ignore the data generated in their plant. This makes it so the organization cannot learn from their mistakes, and repeating the same problems time and again. A machine may give signals of failure, but without a system collecting and studying those signals, the machine will break down at the worst time.
Thanks to data, manufacturers can discover new information, and spot patterns enabling them to improve processes, boost efficiency and identify the main variables affecting production.
Solutions for mitigating unplanned stops
Idle time analysis
Without precise data about idle time, it is difficult to prioritize improvement actions. Operators are important actors when it comes to the causes of unplanned stops. Therefore, it is essential to document the reasons for such stops.
Operators must be capable to record in a simple fashion various reasons for stop, such as:
- Maintenance stop
- Part replacement stop
- Breakdown stop
- Cleaning stop
- Lack of material stop
Traditionally, Excel documents or even paper has been used to gather this information, which was later manually imported into an ERP or MES system. This method is prone to inaccuracies and tedious, and oftentimes data is entered at the end of the shift, with many missing details that could be the key to extract relevant insights.
To guarantee precision of information, it is necessary to automate data gathering through a system that allows operators to input the reasons for stops in an agile and concise fashion.
But not only is operator input data required, in order to complete this information, it is also necessary to collect machine data, such as detailed process data, condition status of certain critical components, etc.
Know your machines and processes in detail
Machine data is objective, quantitative, and a factor to complete and contextualize external data gathered about the stop.
For instance, if a plant collects machine status data and any alarms raised round the clock, these can be correlated with external data (stop reasons, shifts, work orders) to gain a higher understanding about the aspects related to machine availability.
This way, it becomes possible to know the reason for the highest number of stops, which are times between failures, and compare distinct periods of time, thus improving machine availability.
It is also possible to learn the shifts with the most stops, analyze said stops and find out their reason.
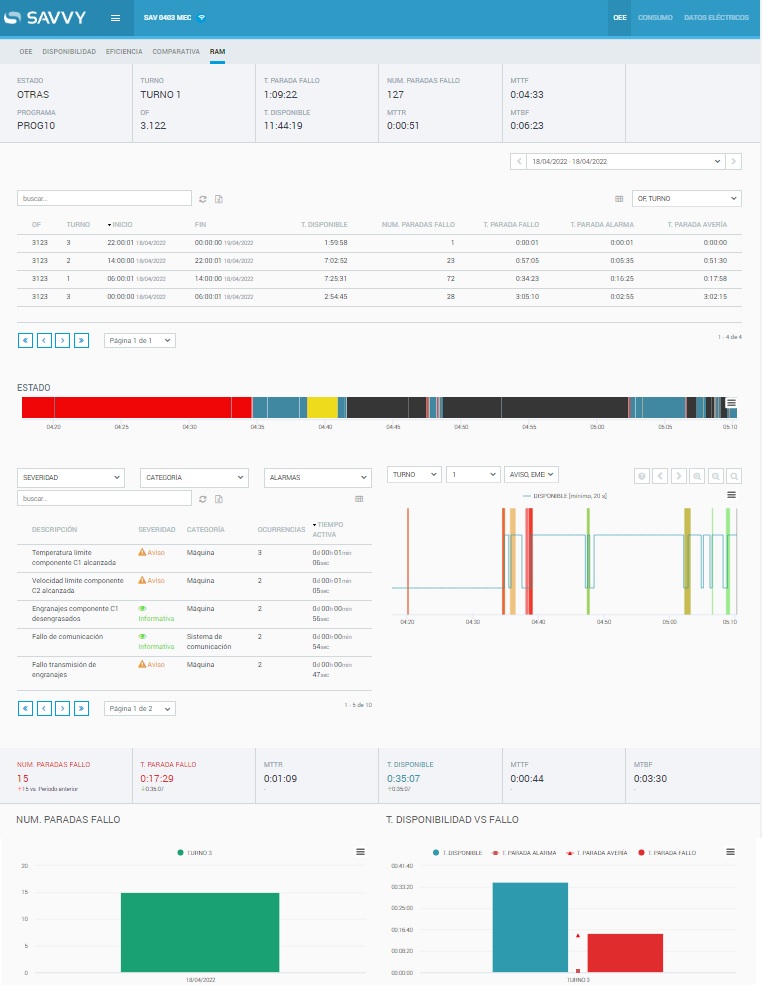 Análisis RAM de paradas – Savvy Manufacturing Intelligence
Análisis RAM de paradas – Savvy Manufacturing Intelligence
Effective producion planning
One of the main points for avoiding plant stops is to carry out an effective production planning. This is essential not just to improve machine availability, but to boost overall plant efficiency.
Production planning is a manufacturing strategy that aims to establish routes and programs that ensure optimal utiilisation of raw materials, workers and machinery.
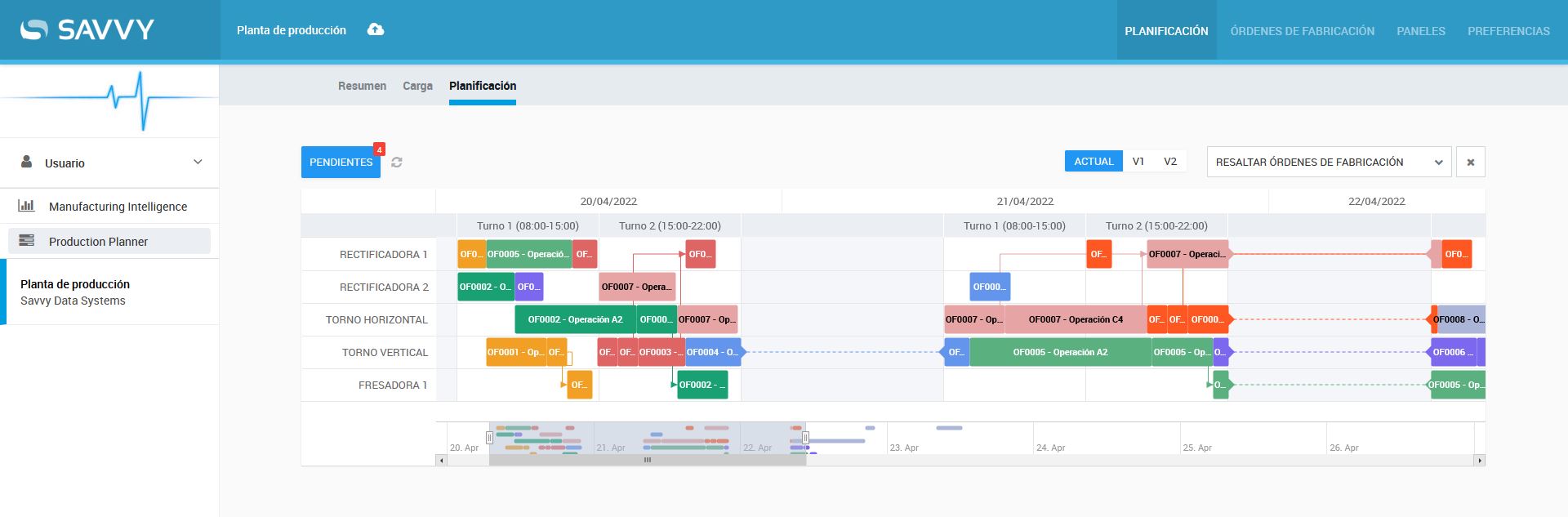
Planificador – Savvy Manufacturing Intelligence
Predictive maintenance
Related to the previous point, the most basic way to prevent unplanned stops is to, precisely, plan stops for preventinve maintenance. Many organizations program their maintenance on specific periods during the work week or minth, but there exist today much more precise methods to plan such maintenances, namely predictive maintenance.
Predictive maintenance allows optimization of preventive maintenance, and reduces corrective maintenance. Through application of anomañy detection algorithms, the company can learn whether a component is beginning to behave in anomalous fashion, for instance due to it beginning to wear out. This way, maintenance staff can plan a stop and properly amend the problem, preventing potential breakdowns and unplanned production stops.
Adequate planning guarantees both staff and machinery are optimally allocated, so that idle time or excessive workloads are reduced. With no effective planning in place, oftentime machines will be stopped despite being available.
As we saw on a previous article, AI (Artificial Intelligence) is slowly becoming a great ally in predictive maintenance projects.
Enable your employees
It is important that employees have a complete vision of what happens in the plant for them to understand how their performance affects end results. For this, they must have access to tools such as the ones described in the points above, since they favour autonomous operation and knowledge-sharing.
It is necessary as well to cover the needs of the plant for knowledge, enablement and communication through a correct knowledge management strategy.
Savvy's Manufacturing Intelligence tools allow manufacturers to gain full control of what happens in their plant. Users can locate maintenance and production problems, and deep-dive into the causes, taking effective measures instantly.